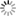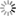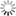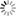Carina Nebula, INAF identifies new star formations
The Gaia-ESO Survey: Global properties of clusters Trumpler 14 and 16 in the Carina nebula study conducted by Francesco Damiani from INAF of Palermo, involving a number of researchers from the INAF observatories of Arcetri, Bologna, Catania, Padua and Palermo, has been recently published in Astronomy & Astrophysics. The study carried out a spectroscopic analysis of a sample of 1085 stars belonging to the Carina region, and in particular to clusters Trumpler 14 and 16.
Stars form in huge clouds of more or less dense gas, which, under the effect of gravity, contracts and form star clusters or associations: there are particularly productive star formation regions that can generate tens of thousands of small stars and a few massive stars.
The Carina Nebula is one of the most interesting regions of massive star formation in the Milky Way, after Cygnus Ob2, the closest to us. In the Nebula, a rich population of stars has formed, which currently includes 14,000 stars already identified, including some massive stars.
The study conducted by Francesco Damiani presents the first spectroscopic analysis of a sample of 1085 stars belonging to Carena, and in particular those belonging to the rich star clusters Trumpler 14 and 16, by using data from the Gaia-Eso Survey. This is how 286 new members have been identified and a detailed analysis has been carried out on the nebula, the stars associated with the region and the chronology of star formation. Moreover, data related to the rotation speed of the stars studied were presented, by highlighting that stars older than 3 million years rotate more slowly than younger stars.
Source: ResearchItaly